Set Up Filtering - Workflow
Here is an overview of the decisions you need to make and the tasks you need to complete to set up filtering for your content.
Decide which filters you are going to use.
Unlike some other products, Paligo does not have one generic filter for everything. Instead, it has a range of different filter types for different purposes. These include filters for language, version, product, market, audience, and more. You need to decide which filters you are going to use.
You can find out about the different types of filter in Types of Filter.
Decide on how you are going to apply the filters to your content.
There are two ways to apply filters:
Use taxonomy tags and drag them on to the topics and components you want to filter. You can only use taxonomy tags to filter entire topics and publications.
Use filter attributes. You add these from the Element attributes panel in the main editor. You can use filter attributes to filter individual block elements, such as paragraphs.
We recommend that you use:
Taxonomy tags for filtering entire topics and subpublications
Filter attributes for filtering block elements inside your topics.
Note
It is possible to only use filter attributes and avoid using taxonomy tags completely. If you choose to do that, be aware that filtering entire topics in this way can be more difficult to manage. With filter attributes, there is no way to apply or edit the filters in bulk —you need to edit each individual topic.
With taxonomy tags, it is easier to manage as you can apply filter tags to topics in bulk.
Create the filter values.
You'll need the filter values for both the filter attributes and taxonomy tags. To create them, you need to add a filter attribute to a topic and then add the values. When you create the values, they are added to the Paligo database. For instructions, see Add the Filter Values.
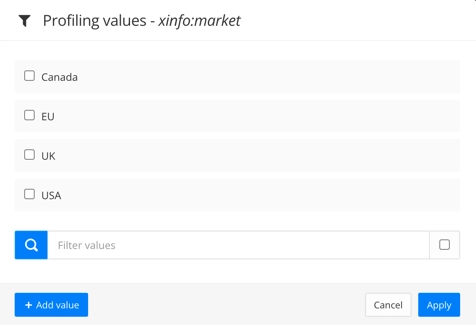
Create the taxonomy tags for filtering.
If you are going to use taxonomy tags for filtering at the topic level or component level, you need to set up a taxonomy hierarchy.
You need one parent taxonomy tag that has the same name as the filter you want to apply, for example, "market". Nested below that as child tags, you need one tag for each of the filter values.
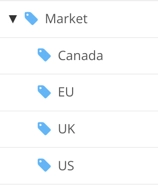
For instructions on creating taxonomy tags for filtering, see Create Taxonomy Tags for Filters.
Enable taxonomies in the output and choose your filtering strategy.
If you are using taxonomy tags for filtering, there are some actions you need to take in the Layout that you will use for publishing:
You have to enable Output taxonomies.
You can choose the taxonomy filter strategy. This affects how Paligo applies the taxonomy filters when you have multiple levels of taxonomy filter tags.
For instructions, see Set the Taxonomy Filter Strategy.
Mark up your content for filtering.
For filter attributes, you need to open the appropriate topic, select the appropriate element and then use the Element attributes panel to add the attribute and value. For instructions, see Apply Filter Attributes.
For filter taxonomy tags, drag the taxonomy tags for the filter values on to the appropriate topics and components. For instructions, see Apply Taxonomy Filter Tags.
Note
When marking up hierarchical structures, like lists and tables, make sure you understand how filters work with hierarchies. Be aware that if you use filters to exclude a parent element, the child elements are automatically excluded too. For details, see Filters on Hierarchical Structures.
Set up Scoped Filtering, if required.
Scoped filtering is for when you reuse the same topic in different places in the same publication. It allows you to filter the topic differently, depending on where it appears in the publication structure. For instructions on how to set it up, see Scoped Filtering.
Start the publishing process and choose the filters you want to apply.
When you publish, you choose the filtering you want Paligo to apply. This is where you decide what content is going to be included or excluded for a particular output (see Choose Which Filters to Apply When Publishing.
The steps above provide a summary of how to set up filtering. You can refer back to this summary whenever you need a reminder on how to set up filtering.
Note that if you want to filter by language, the process is different (see Filter by Language).